Observatory for Educational Resilience in Latin America and the Caribbean
Latest news
What is AdaptED?
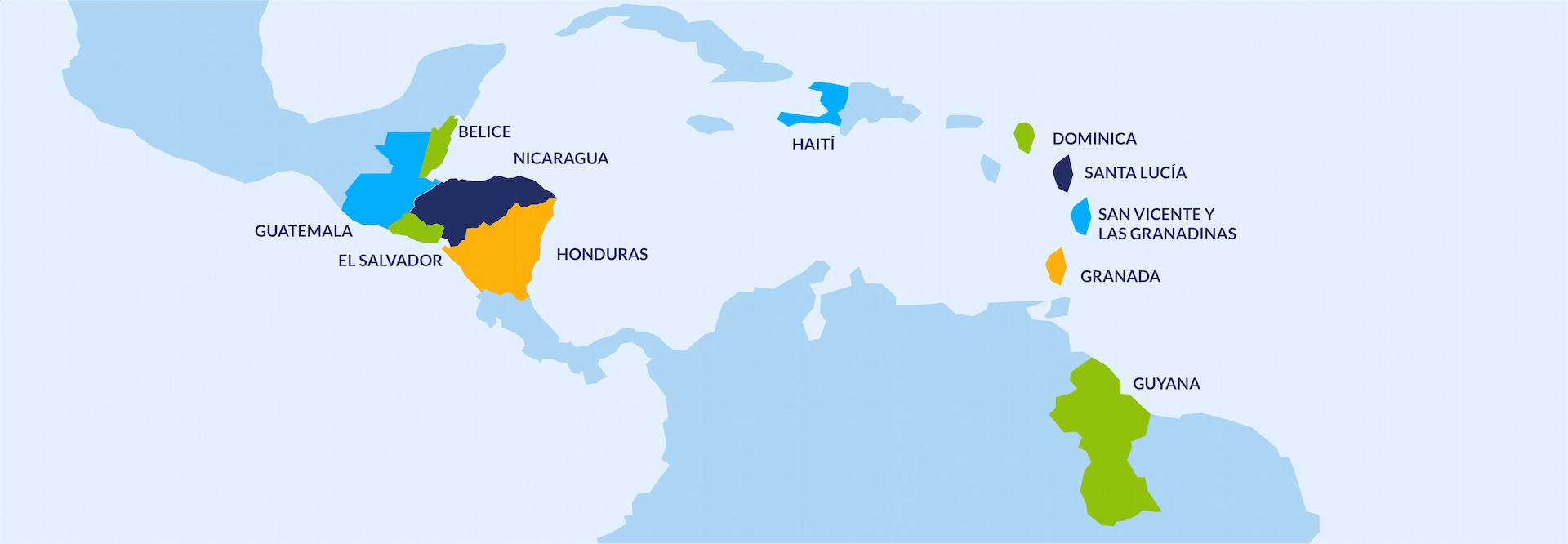
The Observatory for Educational Resilience in Latin America and the Caribbean, AdaptED, is a project that seeks to produce knowledge to support countries in the region in fostering dialogue within their education systems, enabling them to improve their adaptive capacity to face emergency scenarios. We work with partner countries of the Global Partnership for Education (GPE): Belize, Dominica, El Salvador, Grenada, Guatemala, Guyana, Haiti, Honduras, Nicaragua, Saint Lucia, and Saint Vincent and the Grenadines.
Objective 1
Identify and analyze the meanings and practices of resilience in the education systems of GPE partner countries in Latin America and the Caribbean.
Objective 2
Explore future scenarios in GPE member countries in the region, with the aim of proposing recommendations to help them prepare for crises and develop tools to respond effectively.
Objective 3
Mobilize the evidence generated among key stakeholders in the education systems of the region, promoting its use and implementation to strengthen educational resilience.
Consortium organizations
Meet the team
Dante Castillo-Canales
Consultant in Innovative Policies and Practices – SUMMA.
dante.castillo@summaedu.org
AdaptED is made possible thanks to the support of:
This work was supported by the Global Partnership for Education Knowledge and Innovation Exchange (GPE KIX), a joint initiative with the International Development Research Centre (IDRC), Canada.


Expected results
Result 1: Mapping of educational resilience capacities and experiences in the region
We will analyze the presence and understanding of the concept of educational resilience in key documents from the 11 countries of interest. We will also identify the capacities to respond to crisis scenarios in the region.
Result 2: Systematization of effective practices in educational resilience.
We will document successful experiences and lessons learned to inform improvements in public policy and school management.
Result 3: Knowledge mobilization.
We will mobilize knowledge for its use and application through accessible resources aimed at education leaders in these countries and other key actors in the educational ecosystem.
Project timeline

Partner Countries
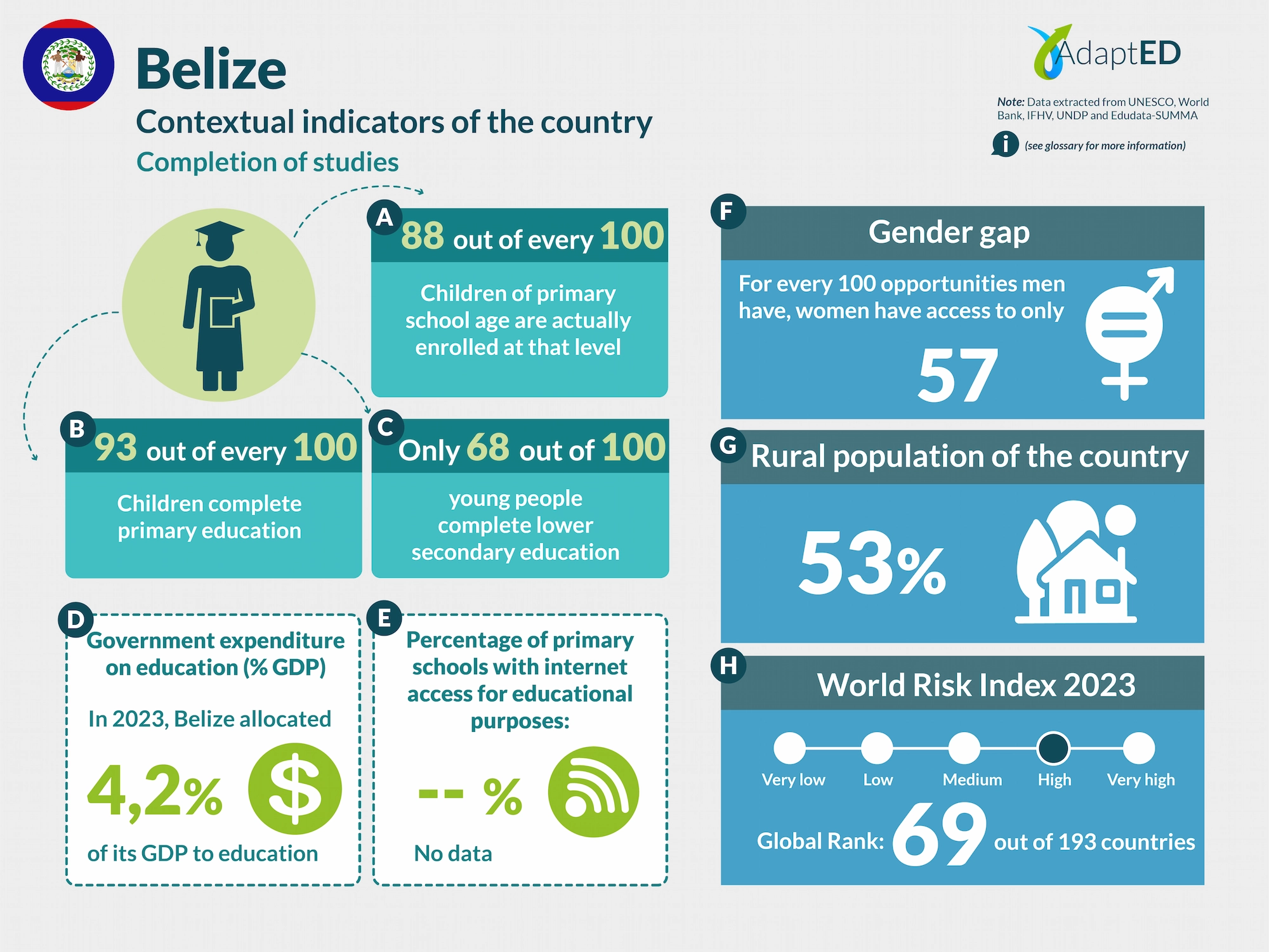

88 de cada 100 niños en edad de cursar primaria están efectivamente matriculados en ese nivel.
*Tasa neta total de matrícula en educación primaria (2023 – Unesco)
Solo 6 de cada 10 jóvenes logran finalizar la educación secundaria inferior.
*Tasa de finalización o culminación escolar – secundaria (2016 – Unicef)
Porcentaje del PIB destinado a educación
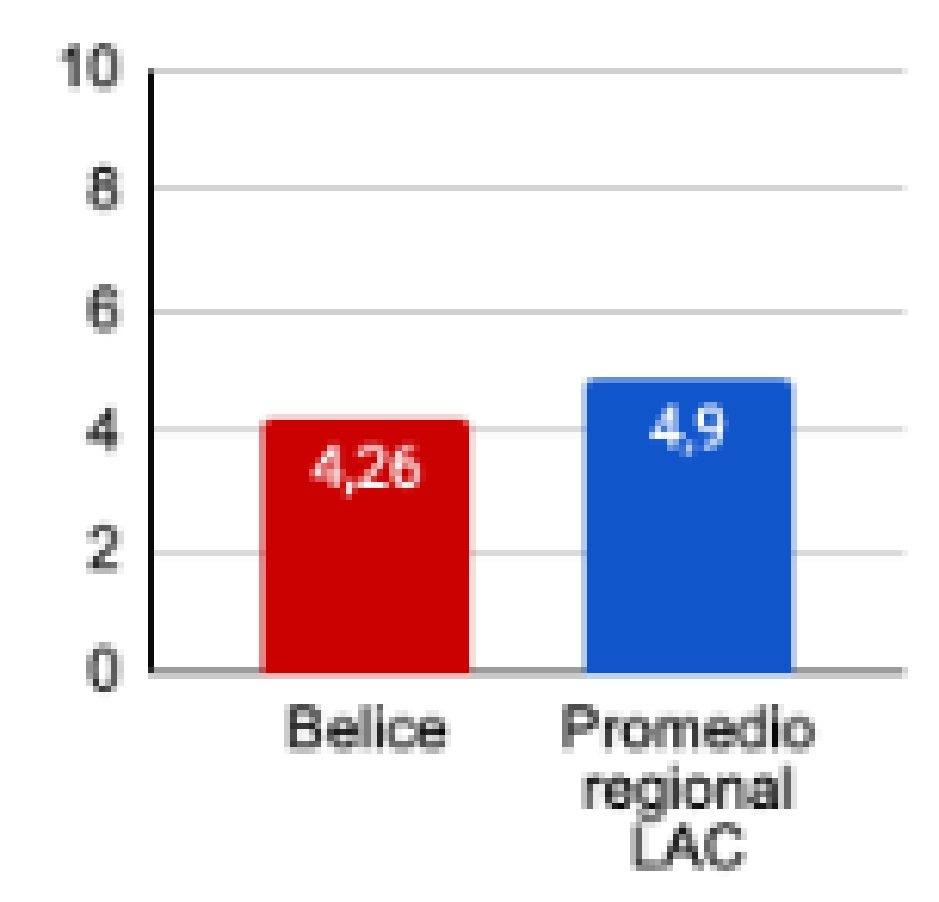
El país destina un porcentaje inferior del PIB comparado con el promedio regional.
*IU – UNESCO
77% de las escuelas primarias y secundarias cuentan con acceso a internet.
**Programa conectED
El 76,4% de los niñas y niños en Belice no logran comprender un texto simple al final de la primaria.
**Banco Mundial
86% de docentes de primaria con formación adecuada.
*Unesco – 2023
170 días sin clases presenciales.
*confirmar
*Existencia de políticas o marcos normativos para la gestión de riesgos
El Plan del Sector Educativo 2021–2025



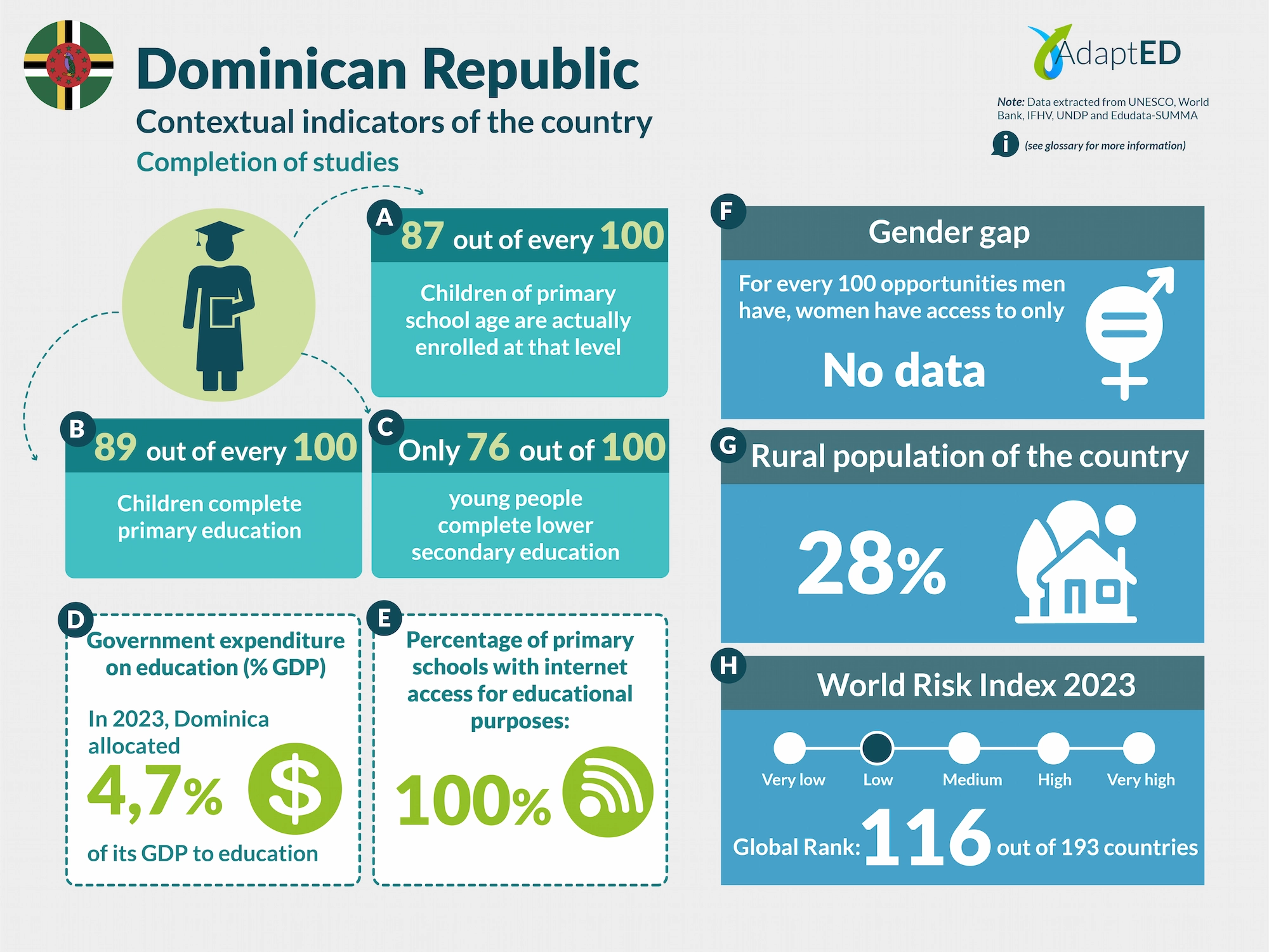
Glossary and Information Sources
School Completion
a. Total Net Enrollment Rate in Primary Education (UNESCO)
Definition: This indicator measures the proportion of children of official primary school age who are actually enrolled in that level, relative to the total primary-age population.
Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
b. Primary Completion Rate (UNESCO)
Definition: Total primary school completion rate. This corresponds to the total number of students entering the last year of primary education, regardless of their age, expressed as a percentage of the total population of official entry age for that grade. This indicator is also called the “gross intake rate for the last grade of primary education.” This rate may be higher than 100% due to children over and under the official entry age entering primary education early or late and/or repeating a grade.
Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
c. Lower secondary completion rate (UNESCO)
Definition: The secondary completion rate is measured as the gross intake rate to the last grade of secondary education (general and pre-vocational). It is calculated by dividing the number of new entrants to the last grade of secondary education, regardless of age, by the population of entry age to the last grade of secondary education.
Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
Education expenditure
d. Public expenditure on education, total (% of GDP) (UNESCO)
Definition: General government expenditure on education (current, capital, and transfers) is expressed as a percentage of GDP. It includes expenditures financed by transfers from international sources to the government. General government generally refers to local, regional, and central governments. Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
Access to Technology in Schools
e. Proportion of schools with internet access for educational purposes (UNESCO)
Definition: Number of schools with internet access for educational purposes, expressed as a percentage of the total number of schools at a given level of education.
Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
Gender Gap
f. Gender Inequality Index (2022 – UNDP)
Definition: Index that seeks to measure gender inequalities in three important aspects of human development: reproductive health, empowerment, and economic status. Its value ranges from 0, when women and men perform equally, to 1, when one gender performs the worst possible across all dimensions measured.
Source: United Nations Development Programme (UNDP). (n.d.). Gender Inequality Index. In Human Development Data Center [Database] https://data.undp.org/es/node/186
Rural Population
g. Percentage of Rural Population (2023 – World Bank)
Definition: The indicator measures the percentage of people living in rural areas within the total population of a country or region.
Source: World Bank (2024). https://datos.bancomundial.org/indicador/SP.RUR.TOTL.ZS?view=chart
World Risk Index
h. World Risk Index 2023 IFHV
Definition: The World Risk Index assesses the latent risk, for 193 countries, that they may be victims of a humanitarian disaster caused by extreme natural events and/or the negative impacts of climate change. It is based on more than 100 high-quality indicators related to vulnerability and exposure to extreme natural events. Values greater than 10 indicate high risk.
Source: Institute for International Law of Peace and Armed Conflict (IFHV)
https://weltrisikobericht.de/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/WRR_2023_english_online161023.pdf
Glossary and Information Sources
School Completion
a. Total Net Enrollment Rate in Primary Education (UNESCO)
Definition: This indicator measures the proportion of children of official primary school age who are actually enrolled in that level, relative to the total primary-age population.
Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
b. Primary Completion Rate (UNESCO)
Definition: Total primary school completion rate. This corresponds to the total number of students entering the last year of primary education, regardless of their age, expressed as a percentage of the total population of official entry age for that grade. This indicator is also called the “gross intake rate for the last grade of primary education.” This rate may be higher than 100% due to children over and under the official entry age entering primary education early or late and/or repeating a grade.
Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
c. Lower secondary completion rate (UNESCO)
Definition: The secondary completion rate is measured as the gross intake rate to the last grade of secondary education (general and pre-vocational). It is calculated by dividing the number of new entrants to the last grade of secondary education, regardless of age, by the population of entry age to the last grade of secondary education.
Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
Education expenditure
d. Public expenditure on education, total (% of GDP) (UNESCO)
Definition: General government expenditure on education (current, capital, and transfers) is expressed as a percentage of GDP. It includes expenditures financed by transfers from international sources to the government. General government generally refers to local, regional, and central governments. Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
Access to Technology in Schools
e. Proportion of schools with internet access for educational purposes (UNESCO)
Definition: Number of schools with internet access for educational purposes, expressed as a percentage of the total number of schools at a given level of education.
Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
Gender Gap
f. Gender Inequality Index (2022 – UNDP)
Definition: Index that seeks to measure gender inequalities in three important aspects of human development: reproductive health, empowerment, and economic status. Its value ranges from 0, when women and men perform equally, to 1, when one gender performs the worst possible across all dimensions measured.
Source: United Nations Development Programme (UNDP). (n.d.). Gender Inequality Index. In Human Development Data Center [Database] https://data.undp.org/es/node/186
Rural Population
g. Percentage of Rural Population (2023 – World Bank)
Definition: The indicator measures the percentage of people living in rural areas within the total population of a country or region.
Source: World Bank (2024). https://datos.bancomundial.org/indicador/SP.RUR.TOTL.ZS?view=chart
World Risk Index
h. World Risk Index 2023 IFHV
Definition: The World Risk Index assesses the latent risk, for 193 countries, that they may be victims of a humanitarian disaster caused by extreme natural events and/or the negative impacts of climate change. It is based on more than 100 high-quality indicators related to vulnerability and exposure to extreme natural events. Values greater than 10 indicate high risk.
Source: Institute for International Law of Peace and Armed Conflict (IFHV)
https://weltrisikobericht.de/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/WRR_2023_english_online161023.pdf
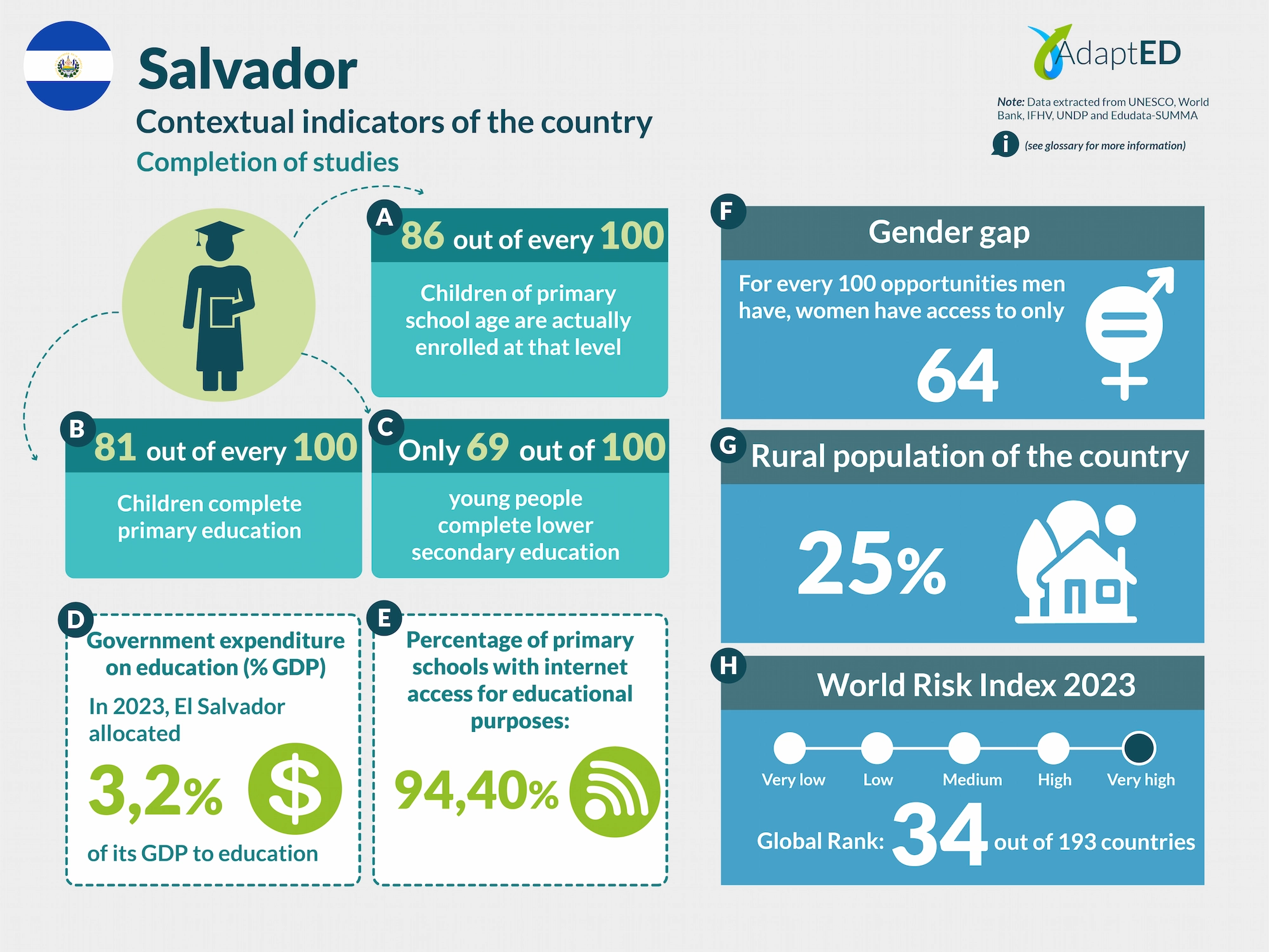
Glossary and Information Sources
School Completion
a. Total Net Enrollment Rate in Primary Education (UNESCO)
Definition: This indicator measures the proportion of children of official primary school age who are actually enrolled in that level, relative to the total primary-age population.
Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
b. Primary Completion Rate (UNESCO)
Definition: Total primary school completion rate. This corresponds to the total number of students entering the last year of primary education, regardless of their age, expressed as a percentage of the total population of official entry age for that grade. This indicator is also called the “gross intake rate for the last grade of primary education.” This rate may be higher than 100% due to children over and under the official entry age entering primary education early or late and/or repeating a grade.
Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
c. Lower secondary completion rate (UNESCO)
Definition: The secondary completion rate is measured as the gross intake rate to the last grade of secondary education (general and pre-vocational). It is calculated by dividing the number of new entrants to the last grade of secondary education, regardless of age, by the population of entry age to the last grade of secondary education.
Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
Education expenditure
d. Public expenditure on education, total (% of GDP) (UNESCO)
Definition: General government expenditure on education (current, capital, and transfers) is expressed as a percentage of GDP. It includes expenditures financed by transfers from international sources to the government. General government generally refers to local, regional, and central governments. Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
Access to Technology in Schools
e. Proportion of schools with internet access for educational purposes (UNESCO)
Definition: Number of schools with internet access for educational purposes, expressed as a percentage of the total number of schools at a given level of education.
Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
Gender Gap
f. Gender Inequality Index (2022 – UNDP)
Definition: Index that seeks to measure gender inequalities in three important aspects of human development: reproductive health, empowerment, and economic status. Its value ranges from 0, when women and men perform equally, to 1, when one gender performs the worst possible across all dimensions measured.
Source: United Nations Development Programme (UNDP). (n.d.). Gender Inequality Index. In Human Development Data Center [Database] https://data.undp.org/es/node/186
Rural Population
g. Percentage of Rural Population (2023 – World Bank)
Definition: The indicator measures the percentage of people living in rural areas within the total population of a country or region.
Source: World Bank (2024). https://datos.bancomundial.org/indicador/SP.RUR.TOTL.ZS?view=chart
World Risk Index
h. World Risk Index 2023 IFHV
Definition: The World Risk Index assesses the latent risk, for 193 countries, that they may be victims of a humanitarian disaster caused by extreme natural events and/or the negative impacts of climate change. It is based on more than 100 high-quality indicators related to vulnerability and exposure to extreme natural events. Values greater than 10 indicate high risk.
Source: Institute for International Law of Peace and Armed Conflict (IFHV)
https://weltrisikobericht.de/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/WRR_2023_english_online161023.pdf
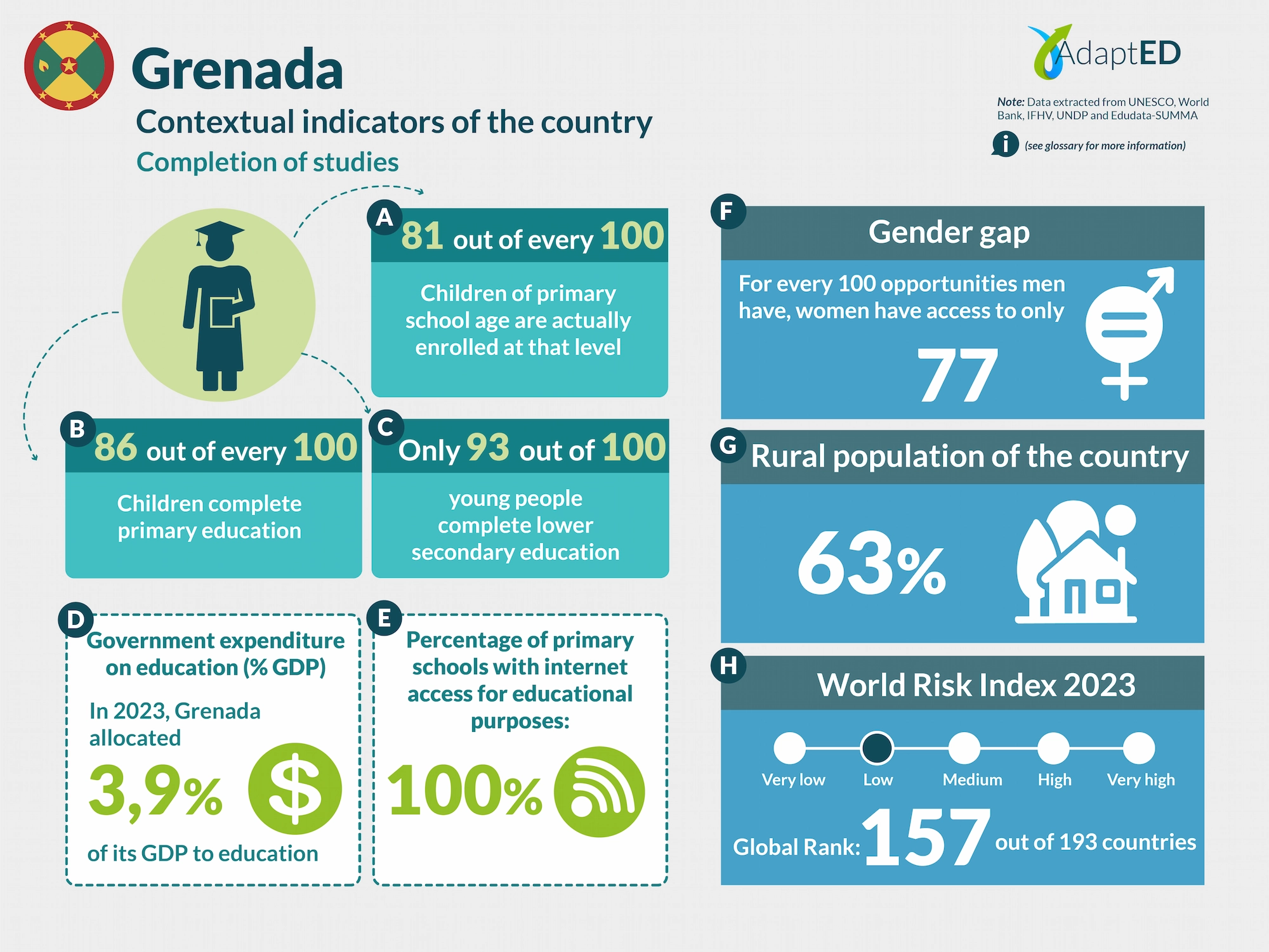
Glossary and Information Sources
School Completion
a. Total Net Enrollment Rate in Primary Education (UNESCO)
Definition: This indicator measures the proportion of children of official primary school age who are actually enrolled in that level, relative to the total primary-age population.
Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
b. Primary Completion Rate (UNESCO)
Definition: Total primary school completion rate. This corresponds to the total number of students entering the last year of primary education, regardless of their age, expressed as a percentage of the total population of official entry age for that grade. This indicator is also called the “gross intake rate for the last grade of primary education.” This rate may be higher than 100% due to children over and under the official entry age entering primary education early or late and/or repeating a grade.
Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
c. Lower secondary completion rate (UNESCO)
Definition: The secondary completion rate is measured as the gross intake rate to the last grade of secondary education (general and pre-vocational). It is calculated by dividing the number of new entrants to the last grade of secondary education, regardless of age, by the population of entry age to the last grade of secondary education.
Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
Education expenditure
d. Public expenditure on education, total (% of GDP) (UNESCO)
Definition: General government expenditure on education (current, capital, and transfers) is expressed as a percentage of GDP. It includes expenditures financed by transfers from international sources to the government. General government generally refers to local, regional, and central governments. Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
Access to Technology in Schools
e. Proportion of schools with internet access for educational purposes (UNESCO)
Definition: Number of schools with internet access for educational purposes, expressed as a percentage of the total number of schools at a given level of education.
Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
Gender Gap
f. Gender Inequality Index (2022 – UNDP)
Definition: Index that seeks to measure gender inequalities in three important aspects of human development: reproductive health, empowerment, and economic status. Its value ranges from 0, when women and men perform equally, to 1, when one gender performs the worst possible across all dimensions measured.
Source: United Nations Development Programme (UNDP). (n.d.). Gender Inequality Index. In Human Development Data Center [Database] https://data.undp.org/es/node/186
Rural Population
g. Percentage of Rural Population (2023 – World Bank)
Definition: The indicator measures the percentage of people living in rural areas within the total population of a country or region.
Source: World Bank (2024). https://datos.bancomundial.org/indicador/SP.RUR.TOTL.ZS?view=chart
World Risk Index
h. World Risk Index 2023 IFHV
Definition: The World Risk Index assesses the latent risk, for 193 countries, that they may be victims of a humanitarian disaster caused by extreme natural events and/or the negative impacts of climate change. It is based on more than 100 high-quality indicators related to vulnerability and exposure to extreme natural events. Values greater than 10 indicate high risk.
Source: Institute for International Law of Peace and Armed Conflict (IFHV)
https://weltrisikobericht.de/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/WRR_2023_english_online161023.pdf
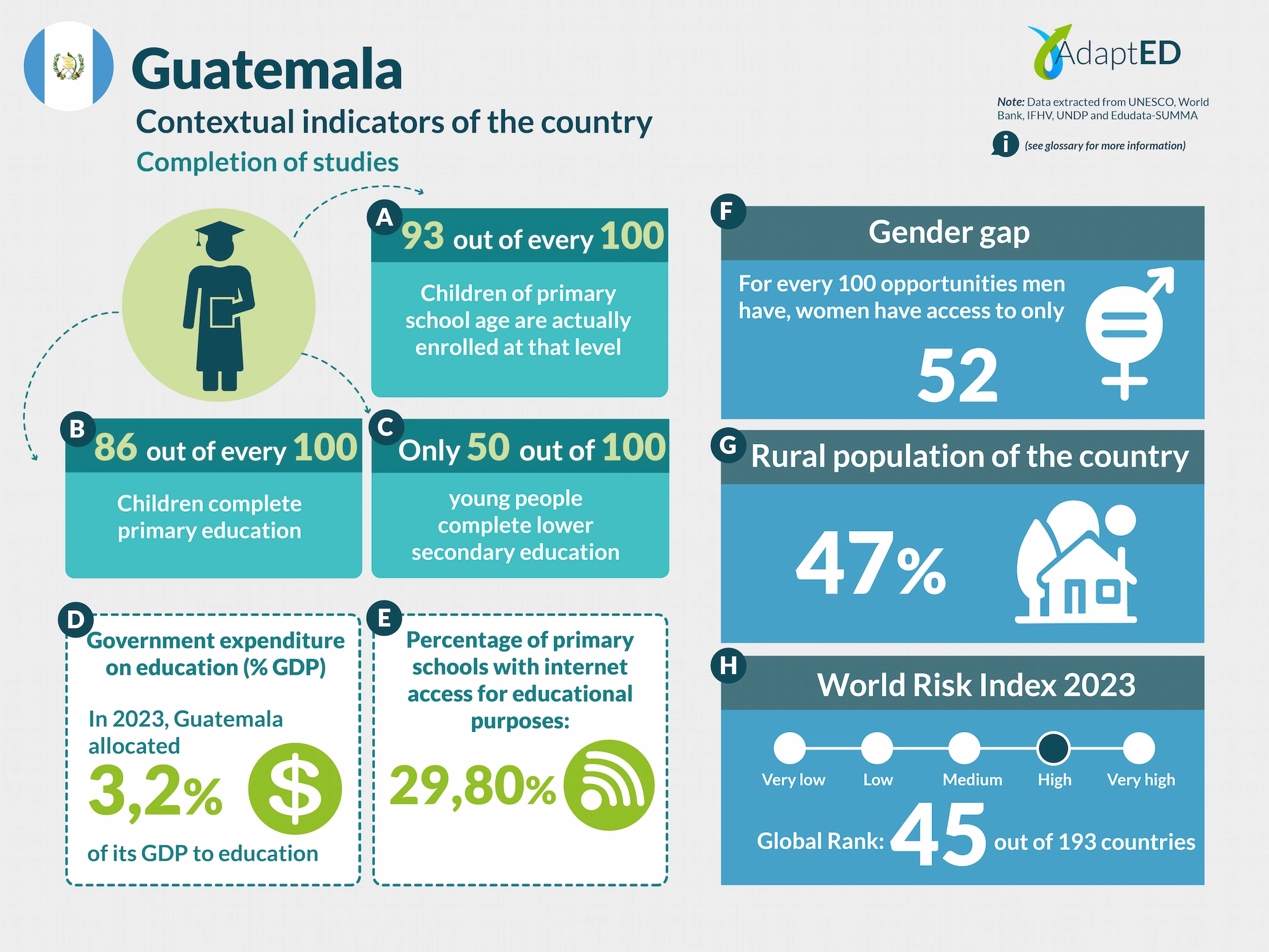
Glossary and Information Sources
School Completion
a. Total Net Enrollment Rate in Primary Education (UNESCO)
Definition: This indicator measures the proportion of children of official primary school age who are actually enrolled in that level, relative to the total primary-age population.
Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
b. Primary Completion Rate (UNESCO)
Definition: Total primary school completion rate. This corresponds to the total number of students entering the last year of primary education, regardless of their age, expressed as a percentage of the total population of official entry age for that grade. This indicator is also called the “gross intake rate for the last grade of primary education.” This rate may be higher than 100% due to children over and under the official entry age entering primary education early or late and/or repeating a grade.
Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
c. Lower secondary completion rate (UNESCO)
Definition: The secondary completion rate is measured as the gross intake rate to the last grade of secondary education (general and pre-vocational). It is calculated by dividing the number of new entrants to the last grade of secondary education, regardless of age, by the population of entry age to the last grade of secondary education.
Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
Education expenditure
d. Public expenditure on education, total (% of GDP) (UNESCO)
Definition: General government expenditure on education (current, capital, and transfers) is expressed as a percentage of GDP. It includes expenditures financed by transfers from international sources to the government. General government generally refers to local, regional, and central governments. Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
Access to Technology in Schools
e. Proportion of schools with internet access for educational purposes (UNESCO)
Definition: Number of schools with internet access for educational purposes, expressed as a percentage of the total number of schools at a given level of education.
Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
Gender Gap
f. Gender Inequality Index (2022 – UNDP)
Definition: Index that seeks to measure gender inequalities in three important aspects of human development: reproductive health, empowerment, and economic status. Its value ranges from 0, when women and men perform equally, to 1, when one gender performs the worst possible across all dimensions measured.
Source: United Nations Development Programme (UNDP). (n.d.). Gender Inequality Index. In Human Development Data Center [Database] https://data.undp.org/es/node/186
Rural Population
g. Percentage of Rural Population (2023 – World Bank)
Definition: The indicator measures the percentage of people living in rural areas within the total population of a country or region.
Source: World Bank (2024). https://datos.bancomundial.org/indicador/SP.RUR.TOTL.ZS?view=chart
World Risk Index
h. World Risk Index 2023 IFHV
Definition: The World Risk Index assesses the latent risk, for 193 countries, that they may be victims of a humanitarian disaster caused by extreme natural events and/or the negative impacts of climate change. It is based on more than 100 high-quality indicators related to vulnerability and exposure to extreme natural events. Values greater than 10 indicate high risk.
Source: Institute for International Law of Peace and Armed Conflict (IFHV)
https://weltrisikobericht.de/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/WRR_2023_english_online161023.pdf
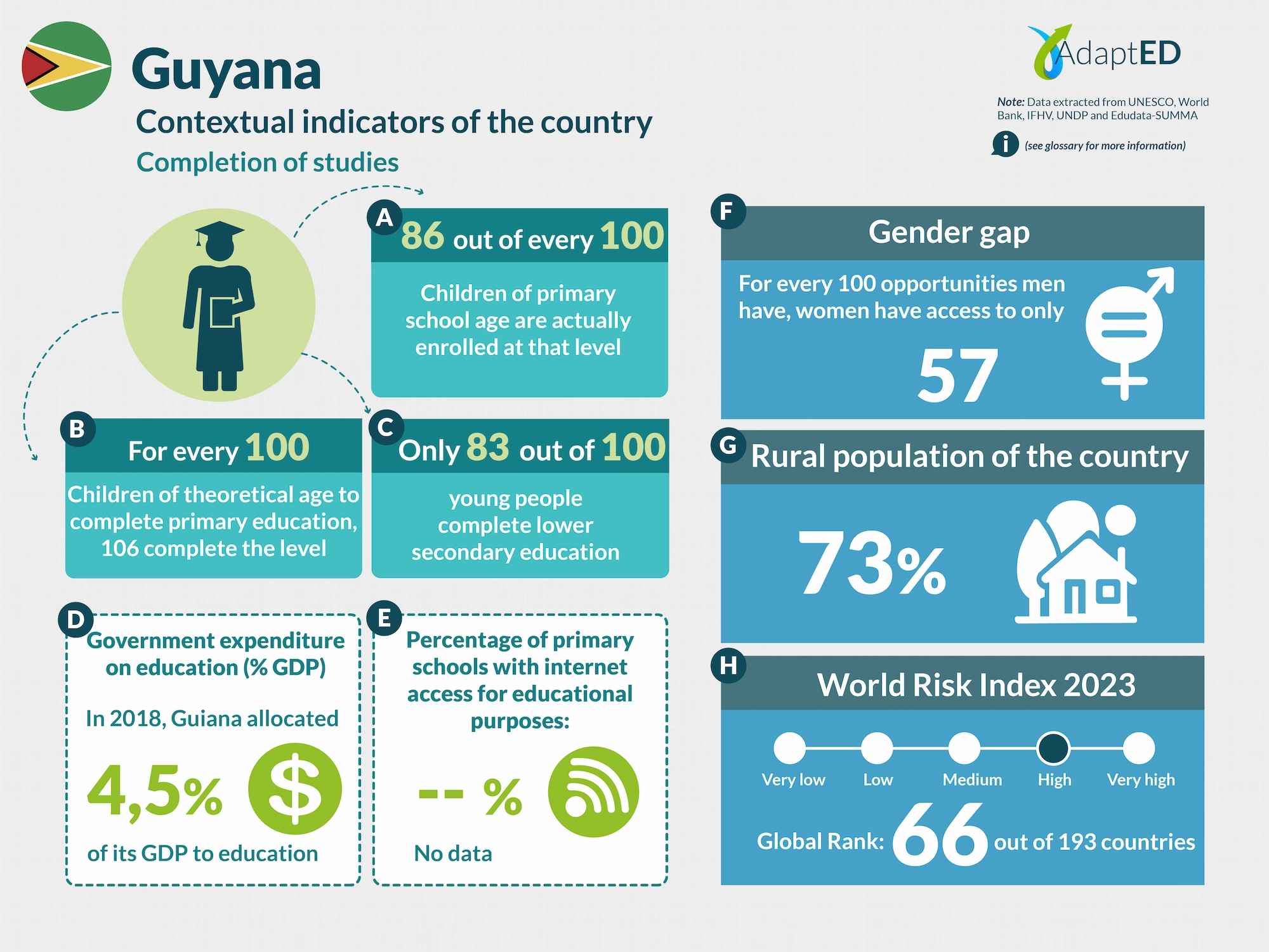
Glossary and Information Sources
School Completion
a. Total Net Enrollment Rate in Primary Education (UNESCO)
Definition: This indicator measures the proportion of children of official primary school age who are actually enrolled in that level, relative to the total primary-age population.
Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
b. Primary Completion Rate (UNESCO)
Definition: Total primary school completion rate. This corresponds to the total number of students entering the last year of primary education, regardless of their age, expressed as a percentage of the total population of official entry age for that grade. This indicator is also called the “gross intake rate for the last grade of primary education.” This rate may be higher than 100% due to children over and under the official entry age entering primary education early or late and/or repeating a grade.
Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
c. Lower secondary completion rate (UNESCO)
Definition: The secondary completion rate is measured as the gross intake rate to the last grade of secondary education (general and pre-vocational). It is calculated by dividing the number of new entrants to the last grade of secondary education, regardless of age, by the population of entry age to the last grade of secondary education.
Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
Education expenditure
d. Public expenditure on education, total (% of GDP) (UNESCO)
Definition: General government expenditure on education (current, capital, and transfers) is expressed as a percentage of GDP. It includes expenditures financed by transfers from international sources to the government. General government generally refers to local, regional, and central governments. Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
Access to Technology in Schools
e. Proportion of schools with internet access for educational purposes (UNESCO)
Definition: Number of schools with internet access for educational purposes, expressed as a percentage of the total number of schools at a given level of education.
Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
Gender Gap
f. Gender Inequality Index (2022 – UNDP)
Definition: Index that seeks to measure gender inequalities in three important aspects of human development: reproductive health, empowerment, and economic status. Its value ranges from 0, when women and men perform equally, to 1, when one gender performs the worst possible across all dimensions measured.
Source: United Nations Development Programme (UNDP). (n.d.). Gender Inequality Index. In Human Development Data Center [Database] https://data.undp.org/es/node/186
Rural Population
g. Percentage of Rural Population (2023 – World Bank)
Definition: The indicator measures the percentage of people living in rural areas within the total population of a country or region.
Source: World Bank (2024). https://datos.bancomundial.org/indicador/SP.RUR.TOTL.ZS?view=chart
World Risk Index
h. World Risk Index 2023 IFHV
Definition: The World Risk Index assesses the latent risk, for 193 countries, that they may be victims of a humanitarian disaster caused by extreme natural events and/or the negative impacts of climate change. It is based on more than 100 high-quality indicators related to vulnerability and exposure to extreme natural events. Values greater than 10 indicate high risk.
Source: Institute for International Law of Peace and Armed Conflict (IFHV)
https://weltrisikobericht.de/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/WRR_2023_english_online161023.pdf
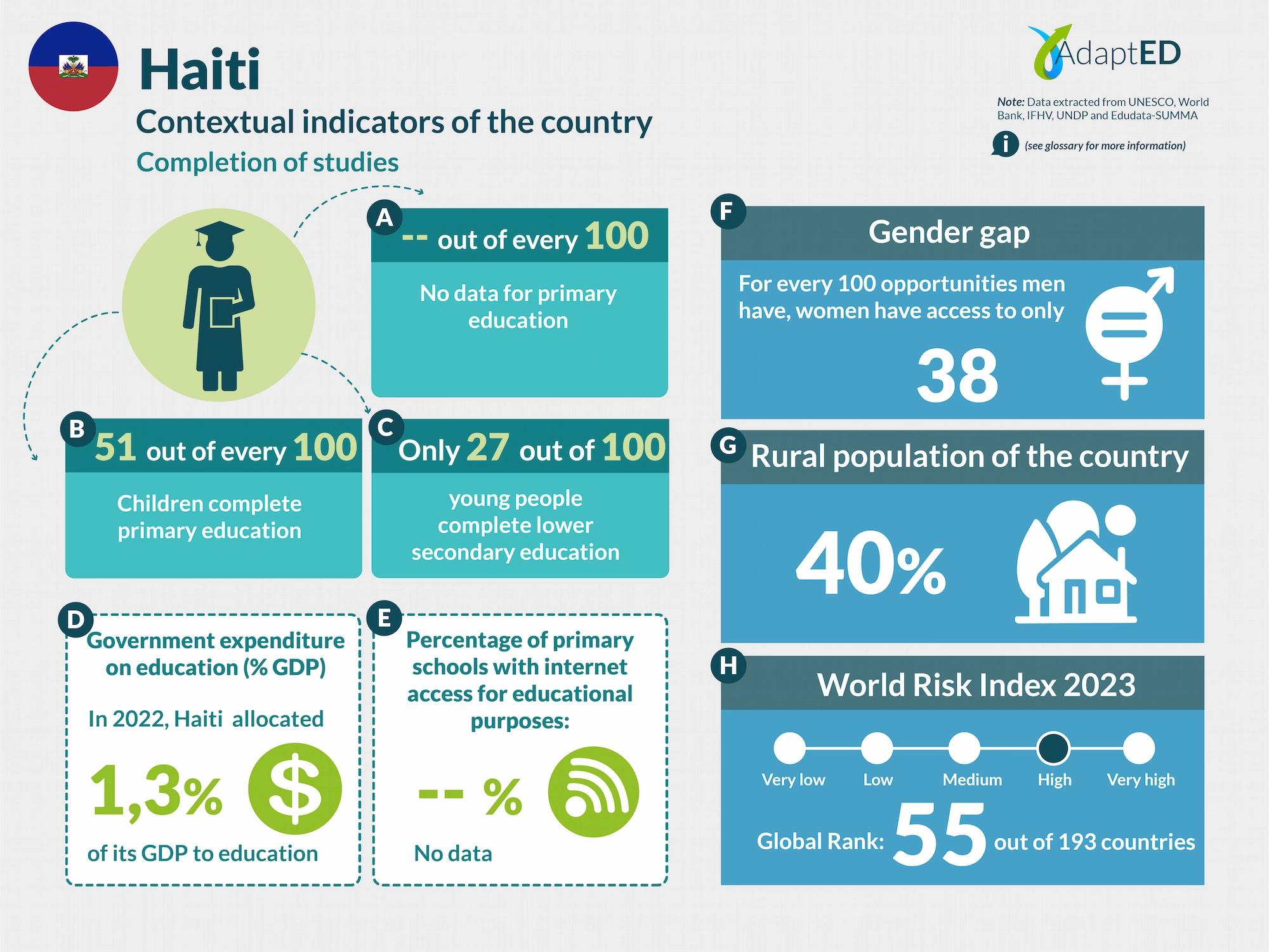
Glossary and Information Sources
School Completion
a. Total Net Enrollment Rate in Primary Education (UNESCO)
Definition: This indicator measures the proportion of children of official primary school age who are actually enrolled in that level, relative to the total primary-age population.
Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
b. Primary Completion Rate (UNESCO)
Definition: Total primary school completion rate. This corresponds to the total number of students entering the last year of primary education, regardless of their age, expressed as a percentage of the total population of official entry age for that grade. This indicator is also called the “gross intake rate for the last grade of primary education.” This rate may be higher than 100% due to children over and under the official entry age entering primary education early or late and/or repeating a grade.
Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
c. Lower secondary completion rate (UNESCO)
Definition: The secondary completion rate is measured as the gross intake rate to the last grade of secondary education (general and pre-vocational). It is calculated by dividing the number of new entrants to the last grade of secondary education, regardless of age, by the population of entry age to the last grade of secondary education.
Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
Education expenditure
d. Public expenditure on education, total (% of GDP) (UNESCO)
Definition: General government expenditure on education (current, capital, and transfers) is expressed as a percentage of GDP. It includes expenditures financed by transfers from international sources to the government. General government generally refers to local, regional, and central governments. Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
Access to Technology in Schools
e. Proportion of schools with internet access for educational purposes (UNESCO)
Definition: Number of schools with internet access for educational purposes, expressed as a percentage of the total number of schools at a given level of education.
Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
Gender Gap
f. Gender Inequality Index (2022 – UNDP)
Definition: Index that seeks to measure gender inequalities in three important aspects of human development: reproductive health, empowerment, and economic status. Its value ranges from 0, when women and men perform equally, to 1, when one gender performs the worst possible across all dimensions measured.
Source: United Nations Development Programme (UNDP). (n.d.). Gender Inequality Index. In Human Development Data Center [Database] https://data.undp.org/es/node/186
Rural Population
g. Percentage of Rural Population (2023 – World Bank)
Definition: The indicator measures the percentage of people living in rural areas within the total population of a country or region.
Source: World Bank (2024). https://datos.bancomundial.org/indicador/SP.RUR.TOTL.ZS?view=chart
World Risk Index
h. World Risk Index 2023 IFHV
Definition: The World Risk Index assesses the latent risk, for 193 countries, that they may be victims of a humanitarian disaster caused by extreme natural events and/or the negative impacts of climate change. It is based on more than 100 high-quality indicators related to vulnerability and exposure to extreme natural events. Values greater than 10 indicate high risk.
Source: Institute for International Law of Peace and Armed Conflict (IFHV)
https://weltrisikobericht.de/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/WRR_2023_english_online161023.pdf
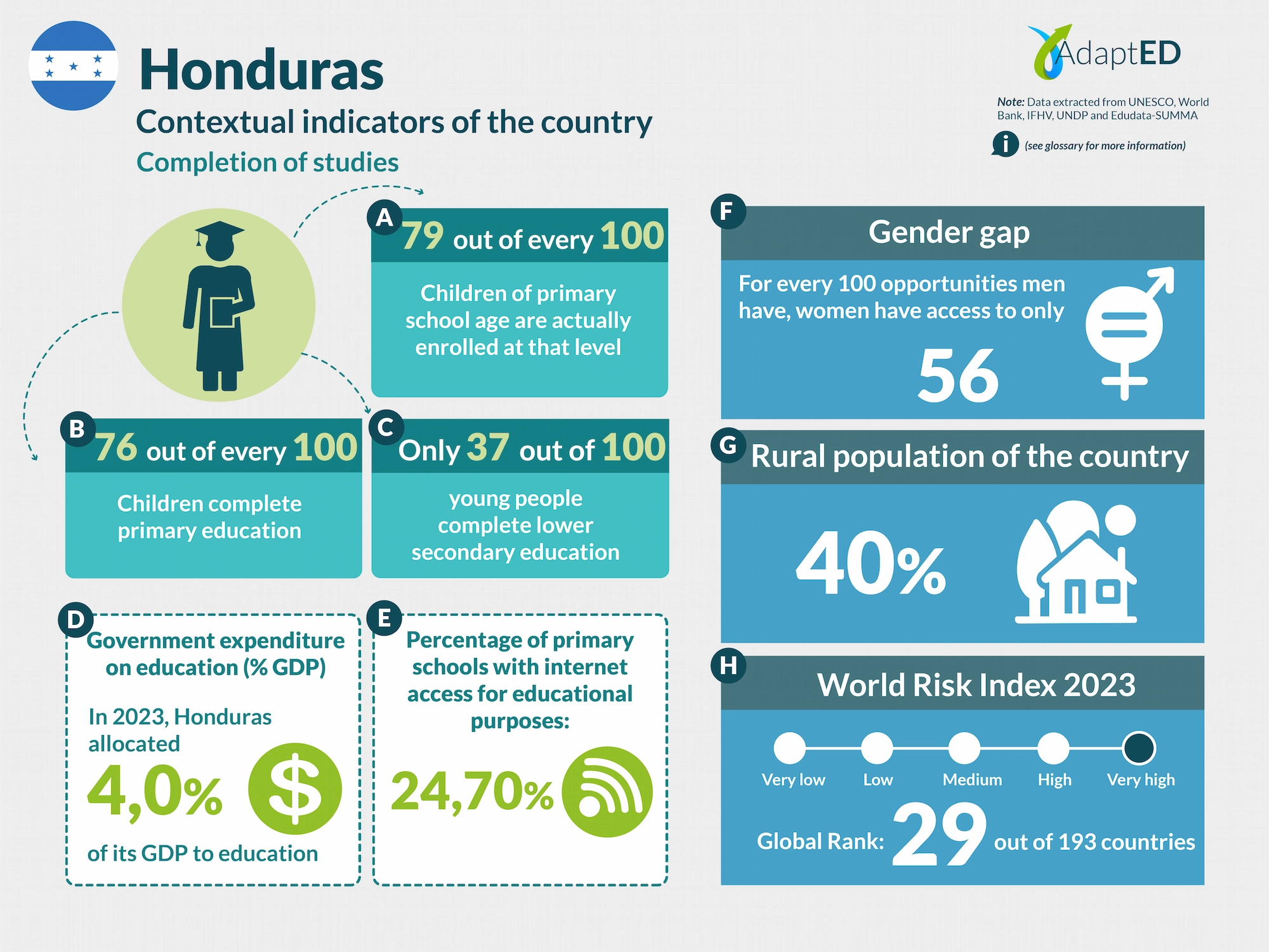
Glossary and Information Sources
School Completion
a. Total Net Enrollment Rate in Primary Education (UNESCO)
Definition: This indicator measures the proportion of children of official primary school age who are actually enrolled in that level, relative to the total primary-age population.
Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
b. Primary Completion Rate (UNESCO)
Definition: Total primary school completion rate. This corresponds to the total number of students entering the last year of primary education, regardless of their age, expressed as a percentage of the total population of official entry age for that grade. This indicator is also called the “gross intake rate for the last grade of primary education.” This rate may be higher than 100% due to children over and under the official entry age entering primary education early or late and/or repeating a grade.
Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
c. Lower secondary completion rate (UNESCO)
Definition: The secondary completion rate is measured as the gross intake rate to the last grade of secondary education (general and pre-vocational). It is calculated by dividing the number of new entrants to the last grade of secondary education, regardless of age, by the population of entry age to the last grade of secondary education.
Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
Education expenditure
d. Public expenditure on education, total (% of GDP) (UNESCO)
Definition: General government expenditure on education (current, capital, and transfers) is expressed as a percentage of GDP. It includes expenditures financed by transfers from international sources to the government. General government generally refers to local, regional, and central governments. Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
Access to Technology in Schools
e. Proportion of schools with internet access for educational purposes (UNESCO)
Definition: Number of schools with internet access for educational purposes, expressed as a percentage of the total number of schools at a given level of education.
Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
Gender Gap
f. Gender Inequality Index (2022 – UNDP)
Definition: Index that seeks to measure gender inequalities in three important aspects of human development: reproductive health, empowerment, and economic status. Its value ranges from 0, when women and men perform equally, to 1, when one gender performs the worst possible across all dimensions measured.
Source: United Nations Development Programme (UNDP). (n.d.). Gender Inequality Index. In Human Development Data Center [Database] https://data.undp.org/es/node/186
Rural Population
g. Percentage of Rural Population (2023 – World Bank)
Definition: The indicator measures the percentage of people living in rural areas within the total population of a country or region.
Source: World Bank (2024). https://datos.bancomundial.org/indicador/SP.RUR.TOTL.ZS?view=chart
World Risk Index
h. World Risk Index 2023 IFHV
Definition: The World Risk Index assesses the latent risk, for 193 countries, that they may be victims of a humanitarian disaster caused by extreme natural events and/or the negative impacts of climate change. It is based on more than 100 high-quality indicators related to vulnerability and exposure to extreme natural events. Values greater than 10 indicate high risk.
Source: Institute for International Law of Peace and Armed Conflict (IFHV)
https://weltrisikobericht.de/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/WRR_2023_english_online161023.pdf
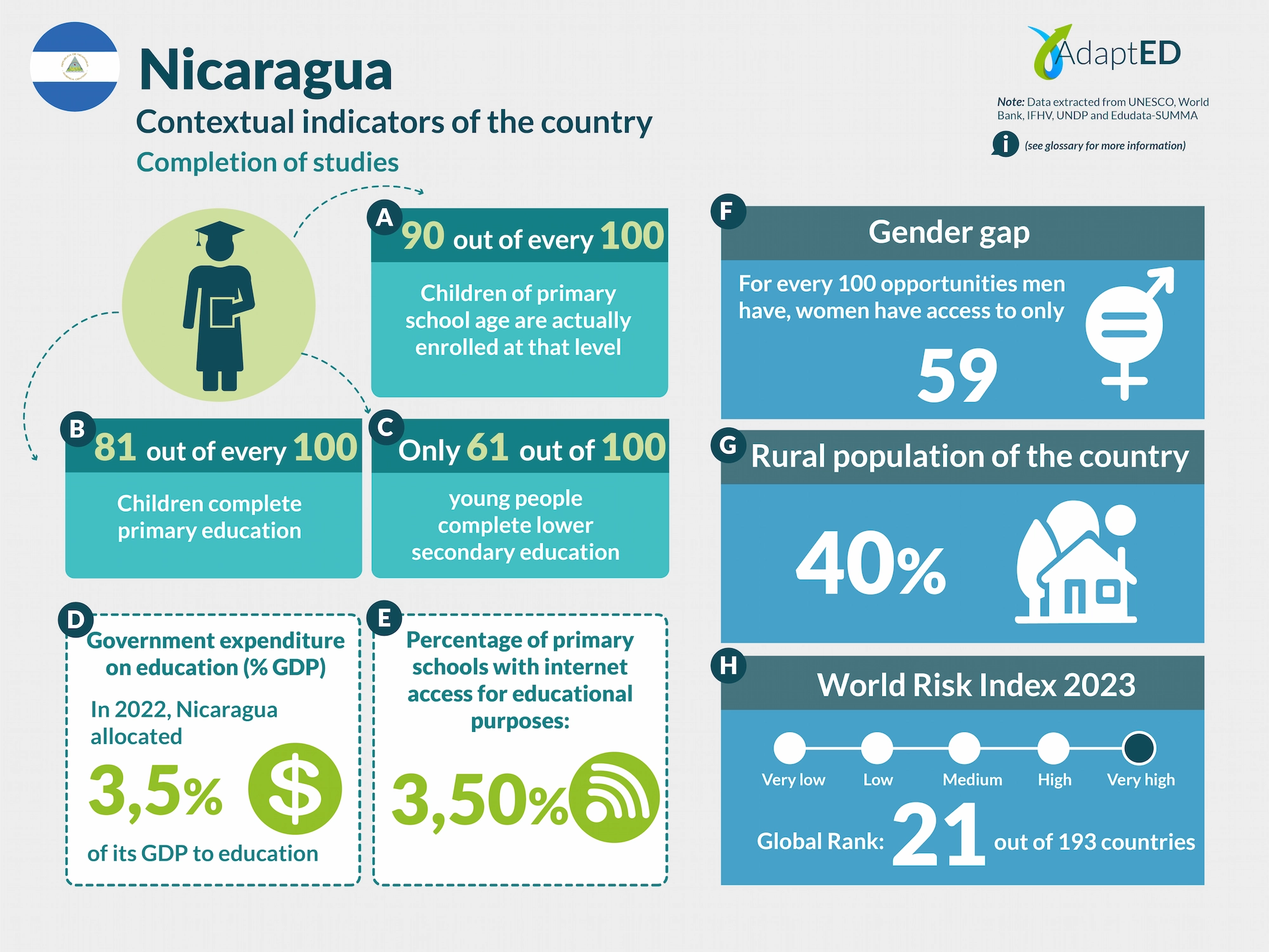
Glossary and Information Sources
School Completion
a. Total Net Enrollment Rate in Primary Education (UNESCO)
Definition: This indicator measures the proportion of children of official primary school age who are actually enrolled in that level, relative to the total primary-age population.
Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
b. Primary Completion Rate (UNESCO)
Definition: Total primary school completion rate. This corresponds to the total number of students entering the last year of primary education, regardless of their age, expressed as a percentage of the total population of official entry age for that grade. This indicator is also called the “gross intake rate for the last grade of primary education.” This rate may be higher than 100% due to children over and under the official entry age entering primary education early or late and/or repeating a grade.
Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
c. Lower secondary completion rate (UNESCO)
Definition: The secondary completion rate is measured as the gross intake rate to the last grade of secondary education (general and pre-vocational). It is calculated by dividing the number of new entrants to the last grade of secondary education, regardless of age, by the population of entry age to the last grade of secondary education.
Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
Education expenditure
d. Public expenditure on education, total (% of GDP) (UNESCO)
Definition: General government expenditure on education (current, capital, and transfers) is expressed as a percentage of GDP. It includes expenditures financed by transfers from international sources to the government. General government generally refers to local, regional, and central governments. Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
Access to Technology in Schools
e. Proportion of schools with internet access for educational purposes (UNESCO)
Definition: Number of schools with internet access for educational purposes, expressed as a percentage of the total number of schools at a given level of education.
Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
Gender Gap
f. Gender Inequality Index (2022 – UNDP)
Definition: Index that seeks to measure gender inequalities in three important aspects of human development: reproductive health, empowerment, and economic status. Its value ranges from 0, when women and men perform equally, to 1, when one gender performs the worst possible across all dimensions measured.
Source: United Nations Development Programme (UNDP). (n.d.). Gender Inequality Index. In Human Development Data Center [Database] https://data.undp.org/es/node/186
Rural Population
g. Percentage of Rural Population (2023 – World Bank)
Definition: The indicator measures the percentage of people living in rural areas within the total population of a country or region.
Source: World Bank (2024). https://datos.bancomundial.org/indicador/SP.RUR.TOTL.ZS?view=chart
World Risk Index
h. World Risk Index 2023 IFHV
Definition: The World Risk Index assesses the latent risk, for 193 countries, that they may be victims of a humanitarian disaster caused by extreme natural events and/or the negative impacts of climate change. It is based on more than 100 high-quality indicators related to vulnerability and exposure to extreme natural events. Values greater than 10 indicate high risk.
Source: Institute for International Law of Peace and Armed Conflict (IFHV)
https://weltrisikobericht.de/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/WRR_2023_english_online161023.pdf
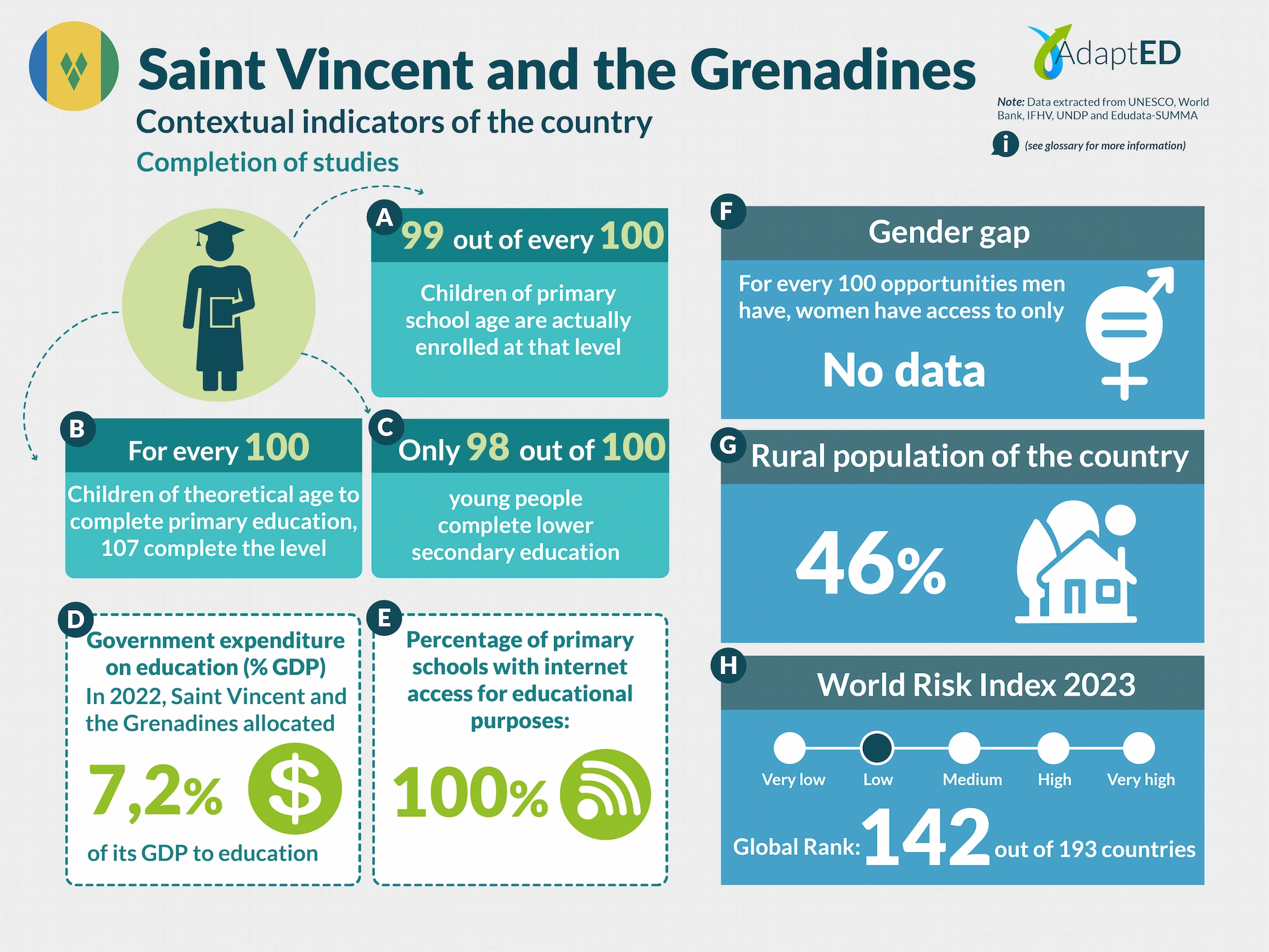
Glossary and Information Sources
School Completion
a. Total Net Enrollment Rate in Primary Education (UNESCO)
Definition: This indicator measures the proportion of children of official primary school age who are actually enrolled in that level, relative to the total primary-age population.
Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
b. Primary Completion Rate (UNESCO)
Definition: Total primary school completion rate. This corresponds to the total number of students entering the last year of primary education, regardless of their age, expressed as a percentage of the total population of official entry age for that grade. This indicator is also called the “gross intake rate for the last grade of primary education.” This rate may be higher than 100% due to children over and under the official entry age entering primary education early or late and/or repeating a grade.
Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
c. Lower secondary completion rate (UNESCO)
Definition: The secondary completion rate is measured as the gross intake rate to the last grade of secondary education (general and pre-vocational). It is calculated by dividing the number of new entrants to the last grade of secondary education, regardless of age, by the population of entry age to the last grade of secondary education.
Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
Education expenditure
d. Public expenditure on education, total (% of GDP) (UNESCO)
Definition: General government expenditure on education (current, capital, and transfers) is expressed as a percentage of GDP. It includes expenditures financed by transfers from international sources to the government. General government generally refers to local, regional, and central governments. Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
Access to Technology in Schools
e. Proportion of schools with internet access for educational purposes (UNESCO)
Definition: Number of schools with internet access for educational purposes, expressed as a percentage of the total number of schools at a given level of education.
Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
Gender Gap
f. Gender Inequality Index (2022 – UNDP)
Definition: Index that seeks to measure gender inequalities in three important aspects of human development: reproductive health, empowerment, and economic status. Its value ranges from 0, when women and men perform equally, to 1, when one gender performs the worst possible across all dimensions measured.
Source: United Nations Development Programme (UNDP). (n.d.). Gender Inequality Index. In Human Development Data Center [Database] https://data.undp.org/es/node/186
Rural Population
g. Percentage of Rural Population (2023 – World Bank)
Definition: The indicator measures the percentage of people living in rural areas within the total population of a country or region.
Source: World Bank (2024). https://datos.bancomundial.org/indicador/SP.RUR.TOTL.ZS?view=chart
World Risk Index
h. World Risk Index 2023 IFHV
Definition: The World Risk Index assesses the latent risk, for 193 countries, that they may be victims of a humanitarian disaster caused by extreme natural events and/or the negative impacts of climate change. It is based on more than 100 high-quality indicators related to vulnerability and exposure to extreme natural events. Values greater than 10 indicate high risk.
Source: Institute for International Law of Peace and Armed Conflict (IFHV)
https://weltrisikobericht.de/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/WRR_2023_english_online161023.pdf
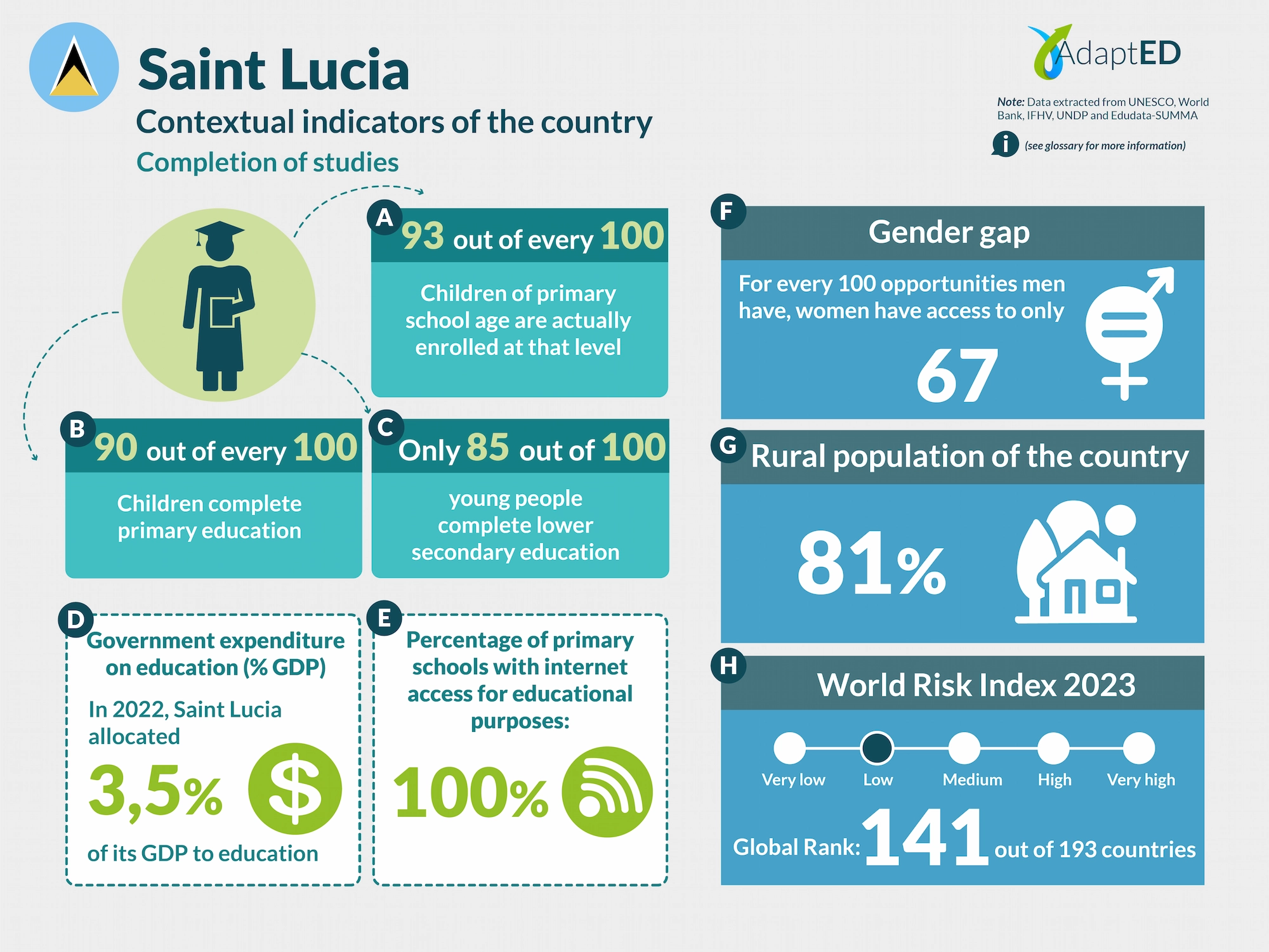
Glossary and Information Sources
School Completion
a. Total Net Enrollment Rate in Primary Education (UNESCO)
Definition: This indicator measures the proportion of children of official primary school age who are actually enrolled in that level, relative to the total primary-age population.
Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
b. Primary Completion Rate (UNESCO)
Definition: Total primary school completion rate. This corresponds to the total number of students entering the last year of primary education, regardless of their age, expressed as a percentage of the total population of official entry age for that grade. This indicator is also called the “gross intake rate for the last grade of primary education.” This rate may be higher than 100% due to children over and under the official entry age entering primary education early or late and/or repeating a grade.
Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
c. Lower secondary completion rate (UNESCO)
Definition: The secondary completion rate is measured as the gross intake rate to the last grade of secondary education (general and pre-vocational). It is calculated by dividing the number of new entrants to the last grade of secondary education, regardless of age, by the population of entry age to the last grade of secondary education.
Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
Education expenditure
d. Public expenditure on education, total (% of GDP) (UNESCO)
Definition: General government expenditure on education (current, capital, and transfers) is expressed as a percentage of GDP. It includes expenditures financed by transfers from international sources to the government. General government generally refers to local, regional, and central governments. Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
Access to Technology in Schools
e. Proportion of schools with internet access for educational purposes (UNESCO)
Definition: Number of schools with internet access for educational purposes, expressed as a percentage of the total number of schools at a given level of education.
Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (2024) https://data.uis.unesco.org/
Gender Gap
f. Gender Inequality Index (2022 – UNDP)
Definition: Index that seeks to measure gender inequalities in three important aspects of human development: reproductive health, empowerment, and economic status. Its value ranges from 0, when women and men perform equally, to 1, when one gender performs the worst possible across all dimensions measured.
Source: United Nations Development Programme (UNDP). (n.d.). Gender Inequality Index. In Human Development Data Center [Database] https://data.undp.org/es/node/186
Rural Population
g. Percentage of Rural Population (2023 – World Bank)
Definition: The indicator measures the percentage of people living in rural areas within the total population of a country or region.
Source: World Bank (2024). https://datos.bancomundial.org/indicador/SP.RUR.TOTL.ZS?view=chart
World Risk Index
h. World Risk Index 2023 IFHV
Definition: The World Risk Index assesses the latent risk, for 193 countries, that they may be victims of a humanitarian disaster caused by extreme natural events and/or the negative impacts of climate change. It is based on more than 100 high-quality indicators related to vulnerability and exposure to extreme natural events. Values greater than 10 indicate high risk.
Source: Institute for International Law of Peace and Armed Conflict (IFHV)
https://weltrisikobericht.de/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/WRR_2023_english_online161023.pdf
Evidence Mobilization
Our goal is to ensure that the knowledge produced by the AdaptED Observatory is accessible, relevant, understandable, and useful for the diverse educational actors in Latin America and the Caribbean. We will promote its use in the design of public policies and educational practices that address the most pressing challenges in the region. To achieve this, we will work in collaboration with the educational community, policymakers, international organizations, universities, and other stakeholders.
AdaptED Resources Coming Soon
Activity Schedule

KIX LAC Hub – REGIONAL MEETING 2025
Fecha: 18 al 20 de junio Lugar: Antigua, Guatemala Garantizando los aprendizajes fundacionales y el desarrollo integral desde la primera…


